Analysts must consider the context within which the company operates, including market conditions and the lifecycle stage of the business. For example, a mature company with established market presence might have a lower ratio compared to a growth-phase company rapidly expanding its sales with fewer assets. Conversely, a declining trend might raise red flags about potential operational stagnation or the obsolescence of assets. A company will gain the most insight when the ratio is compared over time to see trends. For instance, a ratio of 1 means that the net sales of a company equals the average total assets for the year.
Managing Uncollected Protection Deposits in Finance

The asset turnover ratio helps investors understand how effectively companies are using their assets to generate sales. Investors use this ratio to compare similar companies in the same sector or group to determine who’s getting the most out of their assets. The asset turnover ratio is calculated by dividing net sales or revenue by the average total assets.
Asset Turnover Ratio Interpretation and Examples
Instead of dividing net sales by total assets, the fixed asset turnover divides net sales by only fixed assets. This variation isolates how efficiently a company is using its capital expenditures, machinery, and heavy equipment to generate revenue. The fixed asset turnover ratio focuses on the long-term outlook of a company as it focuses on how well long-term investments in operations are performing. This ratio compares net sales displayed on the income statement to fixed assets on the balance sheet.
- A higher fixed asset turnover ratio indicates that a company has effectively used investments in fixed assets to generate sales.
- Plus, the asset turnover ratio can come in handy when you’re looking into business funding.
- The following article will help you understand what total asset turnover is and how to calculate it using the total asset turnover ratio formula.
- The Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio (FAT) is found by dividing net sales by the average balance of fixed assets.
Fixed vs. Total Assets
The asset turnover ratio indicates the efficiency with which a company is using its assets to generate revenue. The asset turnover ratio stands as a critical gauge for investors and analysts aiming to understand the efficiency with which a company utilizes its assets to generate revenue. This metric offers insights into operational performance, revealing how effectively management is at deploying resources to support sales. how to track your small business expenses in 7 easy steps There are other turnover ratios, such as the fixed assets turnover ratio and working capital turnover ratio. In all cases the numerator is the same i.e. net sales (both cash and credit) but denominator is average total assets, average fixed assets, and average working capital, respectively. The total asset turnover ratio is a general efficiency ratio that measures how efficiently a company uses all of its assets.
Asset Turnover vs. Fixed Asset Turnover
Irrespective of whether the total or fixed variation is used, the asset turnover ratio is not practical as a standalone metric without a point of reference. Just-in-time (JIT) inventory management, for instance, is a system whereby a firm receives inputs as close as possible to when they are needed. So, if a car assembly plant needs to install airbags, it does not keep a stock of airbags on its shelves but receives them as those cars come onto the assembly line. But even if your asset turnover ratio number isn’t where you want it to be, don’t worry—that number isn’t set in stone. If you can make adjustments in your processes to improve that number, that’s great news—it shows that you’re a flexible owner, and can make changes to benefit your business. Tighter control of inventory, including returns and damaged goods, will help you bring up your net sales number (and lower your cost of goods sold) and ultimately increase your assets turnover ratio.
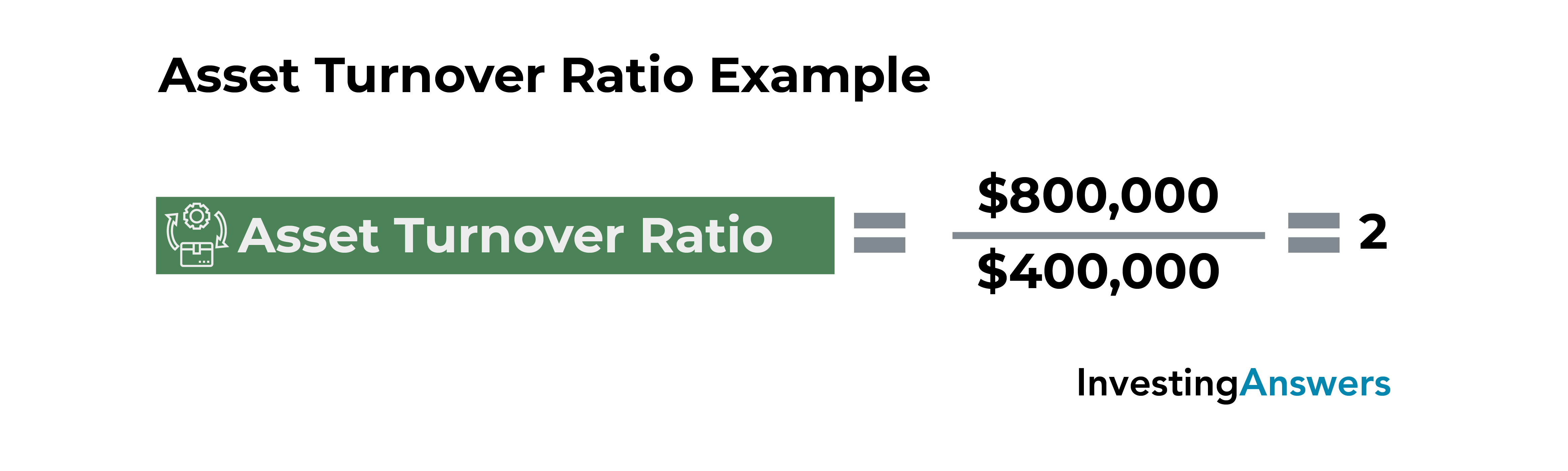
Formula and Calculation of the Asset Turnover Ratio
However, it could also mean that Target, Inc. may not be using its assets efficiently; probably the company’s fixed assets could be sitting idle or not being utilized to their full capacity. This is a good ratio for the company because it indicates that the company can generate enough revenue for itself. However, interpreting this value as being good will also depend on the average asset turnover ratio of the industry to which the company belongs. It is generally preferable for the interpretation of asset turnover ratio to be a higher value.
Walmart and Target have a high asset turnover ratio because they are both in the retail industry. Publicly-facing industries such as retail and restaurants tend to have a higher asset turnover ratio. This explains why the asset turnover ratio of Walmart and Target is way higher than Verizon and AT &T for the same year. As we can see from the calculation done, Verizon and AT&T both had an asset turnover ratio of less than one. In as much as this is considered a low ratio, it is not a bad thing because of the business sector that these companies belong to.
It serves as a barometer for gauging the pulse of a company’s operational prowess. When a firm exhibits a high asset turnover ratio, it often implies that the company is utilizing its assets efficiently to generate sales. This efficiency can be a signal to investors that the company’s management is adept at converting investments into profitable returns.